Functional Movement Therapy (FMT)(RockTape)
FMT Blades / IASTM
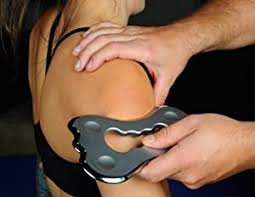
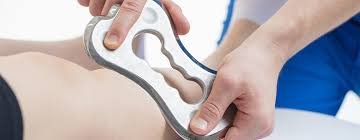
FMT Blades; Instrument Assisted Soft Tissue Mobilization (IASTM) Introduces the concept of mechanical gliding of skin, fascia, and nerve. Also presents concepts of neuro-sensory pain modulation via Instrument Assisted Soft Tissue Mobilization. IASTM tools are designed to be used with very gentle applications of force (aggressive techniques with heavy pressure are no longer required).
The term IASTM or “Instrument Assisted Soft Tissue Manipulation” is commonly paired with the image of steel tools and deep tissue work that can cause redness and bruising on the skin. Current evidence informs us that IASTM techniques don’t need to be aggressive to deliver superior patient outcomes, the tools may be hard, but the techniques are soft.
FMT Vibration Specialist
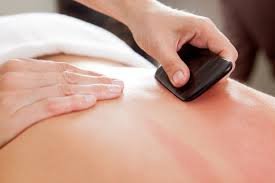
FMT Vibration combines manual therapy and vibration science to create simple and effective non-opioid, neuro-musculoskeletal (NMSK) treatment and self-care.
Using vibration-based therapies are effective interventions for pain management, improving mobility and movement dynamics. A holistic (whole person) approach to movement and functional rehabilitation presented to aid in identifying key areas of compromise within the NMSK system. Is an evidence-informed rehabilitation program that redefines the understanding of the effects of vibration in conjunction with traditional manual therapies (myofascial cupping, local/targeted massage) on pain mitigation, injury recovery/prevention and movement.
The primary goal is to identify and address common NMSK injuries with an innovative functional reappraisal process that includes an external and internal remapping process to help a patient/client reengage in meaningful movement with more confidence and less discomfort.
FMT RockFloss (Compression Band Flossing)
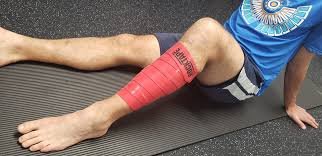
The FMT RockFloss introduces the use of compression floss bands to help reduce tissue edema, improve movement and modulate discomfort. The effects of compression band flossing on connective tissue gliding, tissue traction and tissue compression. Relevant anatomy, physiology and neurology of influenced tissues will be discussed. Interventions with compression band floss (including direction and pressure concepts) will be reviewed and integrated into current rehabilitative concepts.
The term ‘flossing’ is commonly associated with the image of a thick rubber band wrapped around an athlete’s large muscles, however; ‘floss bands’ are an excellent tool for clinical care and a valuable tool for your patient’s and athlete’s self-care programs.